Conjugation verb voyager in French
Model : manger
Auxiliary : avoir
Other forms: se voyager / ne pas voyager / ne pas se voyager
Verbs ending in -ger keep the "e" after "g" if they it is followed by vowels "a" or "o": il mangeait, nous mangeons.
- il/elle voyage
- nous voyageons
- vous voyagez
- ils/elles voyagent
- je voyageais
- tu voyageais
- il/elle voyageait
- nous voyagions
- vous voyagiez
- ils/elles voyageaient
- je voyagerai
- tu voyageras
- il/elle voyagera
- nous voyagerons
- vous voyagerez
- ils/elles voyageront
Passé simple
- je voyageai
- tu voyageas
- il/elle voyagea
- nous voyageâmes
- vous voyageâtes
- ils/elles voyagèrent
Passé composé
- j' ai voyagé
- tu as voyagé
- il/elle a voyagé
- nous avons voyagé
- vous avez voyagé
- ils/elles ont voyagé
Plus-que-parfait
- j' avais voyagé
- tu avais voyagé
- il/elle avait voyagé
- nous avions voyagé
- vous aviez voyagé
- ils/elles avaient voyagé
Passé antérieur
- j' eus voyagé
- tu eus voyagé
- il/elle eut voyagé
- nous eûmes voyagé
- vous eûtes voyagé
- ils/elles eurent voyagé
Futur antérieur
- j' aurai voyagé
- tu auras voyagé
- il/elle aura voyagé
- nous aurons voyagé
- vous aurez voyagé
- ils/elles auront voyagé
- que je voyage
- que tu voyages
- qu' il/elle voyage
- que nous voyagions
- que vous voyagiez
- qu' ils/elles voyagent
- que je voyageasse
- que tu voyageasses
- qu' il/elle voyageât
- que nous voyageassions
- que vous voyageassiez
- qu' ils/elles voyageassent
- que j' eusse voyagé
- que tu eusses voyagé
- qu' il/elle eût voyagé
- que nous eussions voyagé
- que vous eussiez voyagé
- qu' ils/elles eussent voyagé
- que j' aie voyagé
- que tu aies voyagé
- qu' il/elle ait voyagé
- que nous ayons voyagé
- que vous ayez voyagé
- qu' ils/elles aient voyagé

Conditionnel
- je voyagerais
- tu voyagerais
- il/elle voyagerait
- nous voyagerions
- vous voyageriez
- ils/elles voyageraient
Passé première forme
- j' aurais voyagé
- tu aurais voyagé
- il/elle aurait voyagé
- nous aurions voyagé
- vous auriez voyagé
- ils/elles auraient voyagé
Passé deuxième forme
- j' eusse voyagé
- tu eusses voyagé
- il/elle eût voyagé
- nous eussions voyagé
- vous eussiez voyagé
- ils/elles eussent voyagé
- ayant voyagé
- masc.sg.: voyagé
- masc.pl.: voyagés
- fém.sg.: voyagée
- fém.pl.: voyagées
- ayons voyagé
- ayez voyagé
- avoir voyagé
Helping millions of people and large organizations communicate more efficiently and precisely in all languages.
- Conjugation voyager
- Exercise voyager
Conjugation French verb voyager
Translation voyager, indicatif (indicative), présent (present), passé composé (present perfect), imparfait (imperfect), plus-que-parfait (pluperfect), passé simple (simple past), passé antérieur (past perfect), futur simple (future), futur antérieur (past future), conditionnel (conditional), passé (perfect), subjonctif (subjunctive), passé (past), impératif (imperative), infinitif (infinitive), participe (participle), gérondif (gerund), synonyms for the verb voyager.


- Voyager conjugation table
- Voyager conjugation rules
- Voyager synonyms
Voyager french definition
Voyager conjugation in all forms, voyager conjugation in all tenses.
- Voyager : verbs with similar conjugation
- Voyager conjugation in indicative
- Voyager conjugation in present indicative
- Voyager conjugation in present perfect indicative
- Voyager conjugation in imperfect indicative
- Voyager conjugation in pluperfect indicative
- Voyager conjugation in simple past indicative
- Voyager conjugation in past perfect indicative
- Voyager conjugation in simple future indicative
- Voyager conjugation in future perfect indicative
- Voyager conjugation in subjunctive
- Voyager conjugation in present subjunctive
- Voyager conjugation in past subjunctive
- Voyager conjugation in imperfect subjunctive
- Voyager conjugation in pluperfect subjunctive
- Voyager conjugation in conditional
- Voyager conjugation in present conditional
- Voyager conjugation in past conditional
- Voyager conjugation in imperative
- Voyager conjugation in present imperative
- Voyager conjugation in past imperative
- Infinitive of french verb Voyager
- Present infinitive of french verb Voyager
- Past infinitive of french verb Voyager
- Participle of french verb voyager
- Present participle of french verb voyager
- Past participle of french verb voyager
- Gerundive of french verb voyager
- Present gerundive of french verb voyager
- Past gerundive of french verb voyager
Common french verbs
- French Conjugation Rules
- French Tenses
- French Verbs
French Auxiliaries Verbs
- French First Group Verbs
- French Second Group Verbs
- French Third Group Verbs
- Most Common French Verbs
- Avoir conjugation
- Être conjugation
- Aimer conjugation
- Manger conjugation
- Finir conjugation
- Partir conjugation
- Aller conjugation
- Faire conjugation
- Dire conjugation
- Lire conjugation
- Voir conjugation
- Venir conjugation
- Pouvoir conjugation
- Prendre conjugation
- Vouloir conjugation
- Devoir conjugation
- Savoir conjugation
- Mettre conjugation
- Present Indicative
- Imperfect Indicative
- Simple Past Indicative
- Simple Future Indicative
- Present Perfect Indicative
- Pluperfect Indicative
- Past Perfect Indicative
- Future Perfect Indicative
- Present Subjunctive
- Past Subjunctive
- Imperfect Subjunctive
- Pluperfect Subjunctive
- Present Conditional
- Past Conditional
- Present Imperative
- Past Imperative
- French Conjugation
- Voyager conjugation
Conjugation of french verb voyager
Present perfect, simple past, past perfect, simple future, future perfect, subjunctive, conditional, voyager french verb, conjugation rules, reflexive form:, negative form:, interrogative form:.
- Voyager french verb conjugation rules
Voyager french synonyms
- Voyager similar verbs conjugation
This is the list of voyager french verb synonyms :
Active voice conjugation
Similar verbs conjugation.
Here is the full list of verbs sharing the same verb conjugation :
List of verbs used as patterns in french conjugation:
Most common first group verbs
Most common second group verbs, most common third group verbs.
- Terms of use
Contact us :

voyager – to travel
French verb conjugation tables.

Sharing is caring!
David Issokson
David Issokson is a lifelong language learner and speaks over seven languages. Of all the languages he speaks, he's the most passionate about French! David has helped hundreds of students to improve their French in his private lessons. When not teaching or writing his French Word of the Day lessons, David enjoys his time skiing, hiking and mountain biking in Victor, Idaho.
See all posts by David Issokson
'voyager' conjugation table in French
Past participle, present perfect, conditional, past historic, future perfect, past anterior, conditional perfect, subjunctive.
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

All FRENCH words that begin with 'V'
- Actualité
- Économie
- Vidéos
- Édition Abonnés

- Liste de verbes
- Version école
- Règles de conjugaison
- Les homophones
- Modèle de verbes
- Verbes particuliers
- Règles d'orthographe
- Règles de grammaire
- Accueil des exercices
- Exercice au hasard
- Orthographe d'un mot
- La ponctuation
- Identification
- Nouvelles contributions
- Récentes
- Sans réponse
- Les nombres en lettres
- Règle d'écriture des nombres
- Blog Le Conjugueur
- Vidéo
- Rechercher un synonyme
- Traduire un texte
Conjugaison | Règles | Exercices | Orthographe | Forum | Nombres | Blog
Conjugaison du verbe voyager
Le verbe voyager est du premier groupe . Le verbe voyager se conjugue avec l'auxiliaire avoir Traduction anglaise : to travel voyager au féminin | voyager ? | ne pas voyager | Imprimer | Exporter vers Word
Conditionnel
Impératif, gérondif, règle du verbe voyager.
Le e des verbes en -ger est conservé après le g devant les voyelles a et o : nous mangeons, tu mangeas afin de maintenir partout le son du g doux. Réciproquement, les verbes en -guer conservent le u à toutes les formes : fatiguant, il fatigue.
Synonyme du verbe voyager
errer - divaguer - rôder - traîner - vagabonder - vadrouiller - flâner - explorer - parcourir - reconnaître - visiter - prospecter - nomadiser - transhumer - migrer - déplacer - naviguer - sillonner - bourlinguer - marcher - aller
Emploi du verbe voyager
Fréquent - Intransitif
Tournure de phrase avec le verbe voyager
Verbes à conjugaison similaire.
arranger - bouger - changer - charger - corriger - déménager - déranger - diriger - engager - envisager - interroger - manger - nager - partager - ranger - voyager
- Slovenščina
- FAQ Technical Questions
- Text Translation
- Vocabulary Trainer
- Online Dictionary
- Login
- Online dictionary
- Products & Shop
- Conjugation
- Vocabulary trainer
- Dictionary API
- Add to home screen
- Browse the dictionaries
- Terms and conditions of use
- Supply chain
- Data Protection Declaration
- Legal notice
- Privacy Settings
- EN');"> English
- FR');"> French
- DE');"> German
- LA');"> Latin
- ES');"> Spanish
Verb Table for voyager
Indicatif • subjonctif • conditionnel • impératif • formes impersonnelles, passé simple, futur simple, passé composé, plus-que-parfait, passé antérieur, futur antérieur, participe présent, participe passé, browse the conjugations (verb tables), look up "voyager" in other languages, links to further information.
You can suggest improvements to this PONS entry here:
We are using the following form field to detect spammers. Please do leave them untouched. Otherwise your message will be regarded as spam. We are sorry for the inconvenience.
My search history
- Most popular
- English ⇄ German
- English ⇄ Slovenian
- German ⇄ Spanish
- German ⇄ French
- German ⇄ Greek
- German ⇄ Polish
- Arabic ⇄ English
- Arabic ⇄ German
- Bulgarian ⇄ English
- Bulgarian ⇄ German
- Chinese ⇄ English
- Chinese ⇄ French
- Chinese ⇄ German
- Chinese ⇄ Spanish
- Croatian ⇄ German
- Czech ⇄ German
- Danish ⇄ German
- Dutch ⇄ German
- Elvish ⇄ German
- English ⇄ Arabic
- English ⇄ Bulgarian
- English ⇄ Chinese
- English ⇄ French
- English ⇄ Italian
- English ⇄ Polish
- English ⇄ Portuguese
- English ⇄ Russian
- English → Serbian
- English ⇄ Spanish
- Finnish ⇄ German
- French ⇄ Chinese
- French ⇄ English
- French ⇄ German
- French ⇄ Italian
- French ⇄ Polish
- French ⇄ Slovenian
- French ⇄ Spanish
- German ⇄ Arabic
- German ⇄ Bulgarian
- German ⇄ Chinese
- German ⇄ Croatian
- German ⇄ Czech
- German ⇄ Danish
- German ⇄ Dutch
- German ⇄ Elvish
- German ⇄ English
- German ⇄ Finnish
- German ⇄ Hungarian
- German → Icelandic
- German ⇄ Italian
- German ⇄ Japanese
- German ⇄ Latin
- German ⇄ Norwegian
- German ⇄ Persian
- German ⇄ Portuguese
- German ⇄ Romanian
- German ⇄ Russian
- German → Serbian
- German ⇄ Slovakian
- German ⇄ Slovenian
- German ⇄ Swedish
- German ⇄ Turkish
- Dictionary of German Spelling
- Greek ⇄ German
- Hungarian ⇄ German
- Italian ⇄ English
- Italian ⇄ French
- Italian ⇄ German
- Italian ⇄ Polish
- Italian ⇄ Slovenian
- Italian ⇄ Spanish
- Japanese ⇄ German
- Latin ⇄ German
- Norwegian ⇄ German
- Persian ⇄ German
- Polish ⇄ English
- Polish ⇄ French
- Polish ⇄ German
- Polish ⇄ Italian
- Polish ⇄ Russian
- Polish ⇄ Spanish
- Portuguese ⇄ English
- Portuguese ⇄ German
- Portuguese ⇄ Spanish
- Romanian ⇄ German
- Russian ⇄ English
- Russian ⇄ German
- Russian ⇄ Polish
- Slovakian ⇄ German
- Slovenian ⇄ English
- Slovenian ⇄ French
- Slovenian ⇄ German
- Slovenian ⇄ Italian
- Slovenian ⇄ Spanish
- Spanish ⇄ Chinese
- Spanish ⇄ English
- Spanish ⇄ French
- Spanish ⇄ German
- Spanish ⇄ Italian
- Spanish ⇄ Polish
- Spanish ⇄ Portuguese
- Spanish ⇄ Slovenian
- Swedish ⇄ German
- Turkish ⇄ German
Identified ad region: ALL Identified country code: RU -->
Online Language Dictionaries
Formes composées / compound tenses, conditionnel.
*Blue letters in conjugations are irregular forms. ( example ) *Red letters in conjugations are exceptions to the model. ( example ) *Grayed conjugations are forms that are extremely rare.
Report a problem.

Conjugation of the French verb voyager
Conjugaison du verbe voyager
Participe passé voyager, sans accord, avec accord, passé composé, plus-que-parfait, passé simple, passé antérieur, futur simple, futur antérieur, conditionnel, synonyme du verbe voyager, traduction voyager.


Select your French level
To personalize your experience.
- Voyager Conjugation
Voyager to travel
Voyager - indicative, voyager - perfect, voyager - subjunctive, voyager - conditional, voyager - imperative (commands).
We notice you're using an ad blocker.
Linguasorb is free and ad supported, without ad revenue we can't exist. Certain features such as audio, directly cost us money and so are disabled for ad block users.
Please disable your ad blocker for this site if you wish to use the premium features.
Alternatively you can become a supporter and remove the ads completely .
French: voyager
French verb 'voyager' conjugated.

Conjugaison du verbe voyager
- Temps simples
- Temps composés
il (elle) voyage
nous voyageons
vous voyagez
ils (elles) voyagent
je voyageais
tu voyageais
il (elle) voyageait
nous voyagions
vous voyagiez
ils (elles) voyageaient

Passé simple
je voyageai
tu voyageas
il (elle) voyagea
nous voyageâmes
vous voyageâtes
ils (elles) voyagèrent
Futur simple
je voyagerai
tu voyageras
il (elle) voyagera
nous voyagerons
vous voyagerez
ils (elles) voyageront
CONDITIONNEL
je voyagerais
tu voyagerais
il (elle) voyagerait
nous voyagerions
vous voyageriez
ils (elles) voyageraient
que je voyage
que tu voyages
qu’il (elle) voyage
que nous voyagions
que vous voyagiez
qu’ils (elles) voyagent
que je voyageasse
que tu voyageasses
qu’il (elle) voyageât
que nous voyageassions
que vous voyageassiez
qu’ils (elles) voyageassent
Passé composé
j’ ai voyagé
tu as voyagé
il (elle) a voyagé
nous avons voyagé
vous avez voyagé
ils (elles) ont voyagé
Plus-que-parfait
j’ avais voyagé
tu avais voyagé
il (elle) avait voyagé
nous avions voyagé
vous aviez voyagé
ils (elles) avaient voyagé
Passé antérieur
j’ eus voyagé
tu eus voyagé
il (elle) eut voyagé
nous eûmes voyagé
vous eûtes voyagé
ils (elles) eurent voyagé
Futur antérieur
j’ aurai voyagé
tu auras voyagé
il (elle) aura voyagé
nous aurons voyagé
vous aurez voyagé
ils (elles) auront voyagé
j’ aurais voyagé
tu aurais voyagé
il (elle) aurait voyagé
nous aurions voyagé
vous auriez voyagé
ils (elles) auraient voyagé
que j’ aie voyagé
que tu aies voyagé
qu’il (elle) ait voyagé
que nous ayons voyagé
que vous ayez voyagé
qu’ils (elles) aient voyagé
que j’ eusse voyagé
que tu eusses voyagé
qu’il (elle) eût voyagé
que nous eussions voyagé
que vous eussiez voyagé
qu’ils (elles) eussent voyagé
ayons voyagé
ayez voyagé
avoir voyagé
ayant voyagé voyagé (invar.)

Speak any language with confidence
Take our quick quiz to start your journey to fluency today, voyager (to travel) conjugation, conjugation of voyager, examples of voyager, more french verbs, similar but longer, other french verbs with the meaning similar to 'travel':, 'travel' in different languages.
Verb conjugation of "voyager" in French
Conjugate the French Verb "Voyager"
- Pronunciation & Conversation
- Resources For Teachers
In French, the verb voyager means "to travel." This is easy to remember if you associate traveling with a voyage. When you want to say things such as "I traveled" or "we are traveling" in French, the verb needs to be conjugated . A short lesson will introduce you to the most basic conjugations of voyager .
The Basic Conjugations of Voyager
Some French verb conjugations are easier than others and voyager falls in the middle. It follows the rules of all verbs that end in - ger and is classified as a spelling change verb .
As you study these conjugations, you'll notice that the e after the g is retained in many places where it would be dropped in others, such as the regular - er verbs . This is because the e is vital to retaining the soft g sound when the infinitive ending begins with an a or o . Without that e , the g would sound like it does in the word gold and that is not a proper pronunciation.
Other than that small change in some of the forms, you'll find that conjugating voyager is rather standard. Begin by committing the basic present, future, and imperfect past tenses to memory as these will be the most useful forms you'll need.
Using the chart, pair the subject pronoun with the appropriate tense for your subject. For instance, "I am traveling" is je voyage and "we will travel" is nous voyagerons .
The Present Participle of Voyager
Once again, the e remains attached to the verb stem when forming voyager 's present participle . The ending - ant is added to create the word voyageant.
Voyager in the Compound Past Tense
You also have the option of using the French compound past tense, known as the passé composé . It can be easier than memorizing all those imperfect forms, though you will need the auxiliary verb avoir and the past participle voyagé .
For this construction, you only need to conjugate avoir in the present tense to fit the subject pronoun. The past participle remains the same no matter the subject and implies that the action happened in the past. For example, "I traveled" is j'ai voyagé and "we traveled" is nous avons voyagé .
More Simple Conjugations of Voyager
While the conjugations above should be every French student's first priority, there are a few more simple conjugations you might need as well. For example, when you want to imply that the action of traveling is uncertain, use the subjunctive . If, however, someone's travels are dependent on something else, you'll use the conditional .
There may also be times when you encounter the passé simple or the imperfect subjunctive . These are most often found in more formal French but are good to know.
Should you find yourself wanting to use voyager in direct commands or short requests, the imperative is useful. This is also easier because there's no need to include the subject pronoun: simplify tu voyage to voyage .
- How to Conjugate the French Verb "Rester" (to Stay)
- How to Conjugate the French Verb "Promener" (to Walk)
- Simple Conjugations of "Partager" (to Share)
- How to Conjugate the French Verb "Nager" (to Swim)
- How to Conjugate "Traverser" (to Cross) in French
- How to Conjugate the French Verb "Nettoyer"
- The Conjugations of "Pluerer" (to Cry) in French
- How to Conjugate "Obéir" (to Obey) in French
- How to Conjugate the French Verb "Payer" (to Pay)
- Learn How to Conjugate "Sécher" (to Dry)
- Simple Conjugations for "Rompre" (to Break) in French
- Learn the Basic Conjugations of "Sonner" (to Sing)
- How to Conjugate "Respecter" in French
- Learn the Simple Conjugates of "Remplir" (to Fill)
- How to Conjugate the French Verb "Réfléchir" (to Reflect)
- How to Conjugate "Ranger" (to Arrange)
Le passé composé: the past tense in French
When to use the passé composé in french, how to conjugate the passé composé in french.
- Participe passé: the French past participle
Avoir or être?
Agreement of the participe passé.
- Lingolia Plus French
What is the passé composé ?
The passé composé is the most important past tense in French. It corresponds to the English simple past (I did, I saw …) or sometimes the present perfect (I have done, I have seen …) .
The passé composé talks about actions that were completed in the past and emphasises their results or consequences in the present.
In spoken language, the passé composé is always used instead of the passé simple . We form the passé composé using the auxiliary verbs avoir or être followed by the past participle (le participe passé ) of the verb.
Learn everything you need to know about the French passé composé with Lingolia’s quick and easy examples, then put your knowledge to the test in the free exercises.

Hier, Michel a rangé son bureau.
Il a décidé de ranger son bureau chaque semaine.
We use the passé composé to talk about one-time, completed actions that took place in the past. This tense places the emphasis on the result or consequences of the action.
Learners of French often find it difficult to know when to use the passé composé and when to use the imperfect tense . Go to our page dedicated to the difference between the imparfait and passé composé to learn when to use which tense, then test yourself in the free exercises.
To conjugate the passé composé we use the present tense of avoir or être as an auxiliary verb, followed by the past participle (participe passé) of the main verb.
In negative sentences , the past participle comes after the second part of the negation (pas) .
For reflexive verbs , the reflexive pronoun comes after the first part of the negation (ne) and before the auxiliary verb (avoir/être) .
To see the conjugation of any French verb in the passé composé go to our verb conjugator .
Participe passé : the French past participle
For regular er/ ir/re -verbs, the past participle is formed as follows:
- If the infinitive ends in -er , the participle ends in é Example: aim er – aim é
- If the infinitive ends in -ir , the participle ends in i Example: fin ir – fin i
- If the infinitive ends in -re , the participle ends in u Example: vend re - vend u
For the irregular verbs, however, we have to look up the past participle form in the list of irregular verbs or check the verb conjugator — or simply learn the forms by heart.
Most verbs construct the passé composé with avoir, however être is used as the auxiliary verb in the following cases:
- with reflexive verbs
- with the following verbs of movement: naître/mourir be born/die , aller/venir go/come , monter/descendre go up/go down , arriver/partir arrive/leave , entrer/sortir enter/go out , apparaître appear , rester stay , retourner return , tomber fall and their related forms such as: revenir come back , rentrer go back in , remonter go back up , redescendre go back down , repartir leave again .
Note: we use avoir when descendre, ( r)entrer, (re)monter, retourner and sortir are followed by a direct object. In this case, the meaning of the verb often changes.
Need a handy trick to remember which verbs take être as their auxiliary in the passé composé ? Check out our page on the difference between avoir and être.
For some verbs, the participe passé has to agree in gender and number with either the subject or the object of the sentence. This agreement is necessary in the following situations:
- When a verb takes être as an auxiliary, the participle agrees in gender and number with the subject. Example: Il est all é dans son bureau. He went to his office. Elle est all ée dans son bureau. She went to her office. Ils sont all és dans leurs bureaux. They went to their offices. Elles sont all ées dans leurs bureaux. They (only women) went to their offices.
- For verbs that take avoir in the passé composé , the participle only agrees in gender and number with a direct object that comes before the verb. This direct object can take three possible forms: a personal pronoun (me, te, le, la, nous, vous, les) , the relative pronoun que , or a noun placed before the verb (usually in questions and exclamations). Example: Il a rangé son bureau . → Il l' a rang é . He cleaned up his office. → He cleaned it (Fr. masc. sing.) up. Il a rangé sa chambre . → Il l' a rang ée . He cleaned up his room.→ He cleaned it (Fr. fem. sing. ) up. Il a rangé ses dossiers . → Il les a rang és . He sorted his files. → He sorted them (Fr. masc. p lural) . Il a rangé ses cartes de visite . → Il les a rang ées . He sorted his business cards.→ He sorted them (Fr. fem. p lural) .
The participe passé does not agree with the subject of the following verbs: se téléphoner to call each other , se parler to talk to each other , se mentir to lie to each other , se plaire (complaire/déplaire) to like each other , se sourire to smile at each other , se rire to laugh at each other , se nuire to hurt each other , se succéder to succeed each other , se suffire to be enough , se ressembler to look like each other , s’en vouloir to be annoyed with each other . This is because the reflexive pronoun is an indirect object. It is used in the sense of “each other” for these verbs.
se rendre compte
Although it is reflexive, the past participle of the verb se rendre compte (to realise) does not agree with the subject of the sentence. This is because the word compte acts as a direct object (se rendre quoi ? → compte).
How good is your French?
Find out with Lingolia’s free grammar test
Take the test!
Maybe later
Passe composé
It is used to express a past event in a discourse that has consequences in the present.
- J’ ai apporté des fleurs à ma femme. (I brought flowers to my wife)
→ This implies that my wife still has these flowers right now.
The compound past also relates a past event that is definitively closed.
- Lors de la Révolution française, la prise de la Bastille s’est déroulée le 14 juillet 1789. (During the French Revolution, the storming of the Bastille took place on July 14, 1789)
→ This event is definitely over.
2.Structure
Some verbs go with the auxiliary “avoir”, some go with the auxiliary “être”. We will learn about this in the next section.
- 2.1.1. Reflexive verbs
In the passé composé tense, the reflexive verb go with the auxiliary verb “être”. The place of “être” is in between the reflexive pronoun and the past participle. When going with “être”, the past participle must agree with the subject of the sentence.
- Je me suis réveillé(e) à 6 heures. (I woke up at 6 o’clock)
- Ils se sont marié s l’année dernière. ( They got married last year)
- Elle s’est promené e dans le parc hier. (She walked in the park yesterday)
- 2.1.2 . I ntransitive verbs of movement or change
The verbs: Devenir (become), Revenir (return), Monter (go up), Rester (stay), Sortir (leave), Venir (come), Aller (go), Naître (be born), Descendre (descend), Entrer (enter), Rentrer (return), Tomber (fall), Retourner (return), Arriver (arrive), Mourir (die), Partir (leave) et Passer (pass) are conjugated with the auxiliary “être” in the past tense. When going with “être”, the past participle must agree with the subject of the sentence.
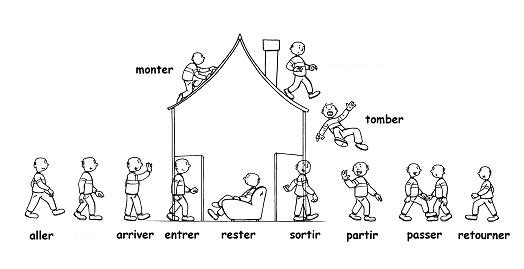
- Je suis allé à l’école. (I went to school)
- Nous sommes parti s de la gare de Bordeau. (We departed from Bordeau station)
- Elles sont arrivé es à l’heure au bureau ? (Did they arrive on time at the office?)
- Il est monté dans sa voiture. (He got in his car)
2.2. The passé composé with “avoir”
Except for reflexive verbs and intransitive verbs of movement or change as above, all the remaining verbs go with the auxiliary verb “avoir”. When going with the auxiliary verb “avoir”, the past participle need not agree with the subject of the sentence.
- Elles ont mangé du chocolat. (They ate chocolate)
- J’ ai acheté une nouvelle chemise. (I bought a new shirt)
- J’ ai fait des croissants. (I made croissants)
- Tu as acheté du pain. (You bought bread)
⚠️ 6 verbs: monter (to go up), descendre (to go down), sortir (to go out), passer (to go through), entrer (to go in) and retourner (to return) as well as its “compound” verbs (remonter, redescendre, rentrer, ressortir, dépasser etc.) can both go with the auxiliary verb AVOIR and can go with the auxiliary verb ÊTRE. These verbs are conjugated with “être” when they don’t have a COD (direct complement). However, these verbs will conjugate with the auxiliary verb “avoir” when they have the direct complement COD.
2.3. The negation
In the negative form, we have the structure:
- Je n’ai pas vu. (I didn’t see)
- Je ne suis pas venu. (I did not come)
- Je ne me suis pas levé tôt. ( I didn’t get up early)
3. Exercises
Exercise 1: Conjugate these verbs in the passé composé
1. Je avoir _________________ soif et je prendre _________________ un café.
2. Tu vouloir _________________ me voir, tu arriver _________________ tôt.
3. Il prendre _________________ son parapluie et il sortir _________________ .
4. Ils aller _________________ en vacances l’été dernier.
5. Il devoir _________________ téléphoner au médecin.
6. Vous étudier _________________ bien et vous réussir _________________ facilement.
7. Nous commencer _________________ un nouveau cours.
8. Ils venir _________________ souvent nous visiter.
9. Vous faire _________________ de l’exercice physique.
10. Tu tousser _________________ continuellement.
11. On devoir _________________ écouter nos parents.
12. Nous réfléchir _________________ et nous choisir _________________ un bonbon.
13. Il pleuvoir _________________ et je attendre _________________ l’autobus.
14. Hier soir, nous manger _________________ tôt.
15. Elles appeler _________________ leurs amis.
16. Ma sœur conduire _________________ vite et mes frères conduire _________________ lentement.
17. Je ouvrir _________________ la porte et le chien courir _________________ à l’extérieur.
18. Elles finir _________________ leurs devoirs et ils sortir _________________ jouer.
19. Il croire _________________ que nous avoir _________________ raison.
20. Le petit chat plaire _________________ à mes parents.
1. J’ai eu soif et j’ai pris un café.
2. Tu as voulu me voir, tu es arrivé(e) tôt.
3. Il a pris son parapluie et il est sorti.
4. Ils sont allés en vacances l’été dernier.
5. Il a dû téléphoner au médecin.
6. Vous avez bien étudié et vous avez réussi facilement.
7. Nous avons commencé un nouveau cours.
8. Ils sont venus souvent nous visiter.
9. Vous avez fait de l’exercice physique.
10. Tu as toussé continuellement.
11. On a dû écouter nos parents.
12. Nous avons réfléchi et nous avons choisi un bonbon.
13. Il a plu et j’ai attendu l’autobus.
14. Hier soir, nous avons mangé tôt.
15. Elles ont appelé leurs amis.
16. Ma sœur a conduit vite et mes frères ont conduit lentement.
17. J’ai ouvert la porte et le chien a couru à l’extérieur.
18. Elles ont fini leurs devoirs et ils sont sortis jouer.
19. Il a cru que nous avons eu raison.
20. Le petit chat a plu à mes parents.
Exercise 2: Conjugate these verbs in the passé composé
1. Quand le téléphone sonner _________________, on répondre _________________ . 2. Alors, tu voir _________________ le film, tu écrire _________________ un texte et tu décrire _________________ l’histoire.
3. Tu ne oublier _________________ pas ! Tu nettoyer _________________ la maison. 4. Le héros mourir _________________ à la fin du film.
5. Vous devoir _________________ de l’argent à tous vos amis.
6. Tu descendre _________________ l’escalier et tu tourner _________________ à gauche.
7. Quand je lire _________________, je découvrir _________________ de nouvelles choses.
8. Je perdre _________________ mon temps : je ne faire _________________ rien.
9. Vous pleurer _________________ beaucoup. Pourquoi ?
10. Mes frères vendre _________________ leurs articles de sport.
11. Nous vouloir _________________ visiter le musée et nous devoir _________________ payer l’entrée.
12. Vous être _________________ une très jolie jeune femme.
13. Ils faire _________________ une grande fête à chaque année.
14. Tu entendre _________________ ce bruit ? Je comprendre _________________ des mots...
15. Tu penser _________________ toujours à ton amoureux.
16. Mes voisins vouloir _________________ quitter le pays.
17. Tu remplir _________________ le pot d’eau et tu mettre _________________ des glaçons.
18. Je promettre _________________ de dire la vérité.
19. Hier soir, je lire _________________ un peu et je dormir _________________ sur le divan.
20. Ils finir _________________ le jardinage et ils rentrer _________________ se laver.
21. Tu envoyer _________________ un message à tes amis.
22. Tu prendre _________________ une douche et tu aller _________________ au lit.
23. Quand je avoir _________________ deux ans, je apprendre _________________ à marcher.
24. Nous vivre _________________ au Canada.
25. Ils faire _________________ à manger et ils nettoyer _________________ toujours la cuisine
1. Quand le téléphone a sonné, on a répondu.
2. Alors, tu as vu le film, tu as écrit un texte et tu as décrit l’histoire.
3. Tu n’as pas oublié ! Tu as nettoyé la maison.
4. Le héros est mort à la fin du film.
5. Vous avez dû de l’argent à tous vos amis.
6. Tu as descendu l’escalier et tu as tourné à gauche.
7. Quand j’ai lu, j’ai découvert de nouvelles choses.
8. J’ai perdu mon temps : je n’ai rien fait.
9. Vous avez beaucoup pleuré. Pourquoi ?
10. Mes frères ont vendu leurs articles de sport.
11. Nous avons voulu visiter le musée et nous avons dû payer l’entrée.
12. Vous avez été une très jolie jeune femme.
13. Ils ont fait une grande fête à chaque année.
14. Tu as entendu ce bruit ? J’ai compris des mots...
15. Tu as toujours pensé à ton amoureux.
16. Mes voisins ont voulu quitter le pays.
17. Tu as rempli le pot d’eau et tu as mis des glaçons.
18. J’ai promis de dire la vérité.
19. Hier soir, j’ai lu un peu et j’ai dormi sur le divan.
20. Ils ont fini le jardinage et ils sont rentrés se laver.
21. Tu as envoyé un message à tes amis.
22. Tu as pris une douche et tu es allé(e) au lit.
23. Quand j’ai eu deux ans, j’ai appris à marcher.
24. Nous avons vécu au Canada.
25. Ils ont fait à manger et ils ont toujours nettoyé la cuisine.
Exercise 3: Conjugate the verbs of this dialogue in the passé composé
– Qu’est-ce que vous (faire) _________________ en août ? Vous (partir) _________________?
– Oui, j’ (voyager) _________________, je (aller) _________________ en Espagne avec mon mari.
– Qu’est-ce que vous (voir) _________________?
– On (aller) _________________ Grenade, Séville, Cordoue.
– Vous (aller) _________________ à l’Alhambra ? Vous (prendre) _________________ des photos ?
– Oui, oui, nous (visiter) _________________ l’Alhambra, nous (entrer) _________________ dans de magnifiques églises. Nous (prendre) _________________ plein de photos.
– Vous (goûter) _________________ la cuisine espagnole ? Ça vous (plaire) _________________?
– Oh oui, nous (adorer) _________________ ! Et toi, qu’est-ce que tu (faire) _________________ ?
– Moi, je (aller) _________________ à Paris, nous (monter) _________________ sur la Tour Eiffel avec les enfants, on (se promener) _________________ dans des jardins. Et on (partir) _________________ une journée à Versailles, où quelqu’un (voler) _________________ mon sac. Nous (devoir) _________________ aller à la police, ça (prendre) _________________ plus de 3h !
– Oh là là ! À part ce problème, tout (bien - se passer) _________________?
– Oui, très bien. Les enfants (être) _________________ très contents de visiter Paris.
avez fait – êtes partis – ai voyagé – suis allée – avez vu – est allés - êtes allés – avez pris – avons visité – sommes entrés – avons pris – avez goûté – a plu – avons adoré – as fait – suis allé(e) – sommes montés – s’est promenés – est partis – a volé – avons dû – a pris– s’est bien passé – ont été
Exercise 4: Conjugate these verbs in the passé composé
1. Pendant les dernières vacances, nous _________________________ au Japon (aller).
2. Ce matin, il ________________________ le bus pour aller à l’école (prendre).
3. L’année dernière, mes parents _______________________________ à Nantes (venir).
4. Lundi dernier, je _______________________________ en retard (se réveiller).
5. Hier soir, j’_________________________________ un bon film (voir).
6. Albert Einstein _______________________ en 1879 (naître).
7. Il _____________________________en 1955 (mourir).
8. Marie Curie ________________________ un Prix Nobel de physique en 1903 (avoir).
9. Obama _____________________ le premier président noir des Etats-Unis (devenir).
10. Picasso _____________________ son célèbre tableau « Guernica » en 1937 (réaliser)
Exercise 5: Put the words in order
1. Il y a 10 minutes – le facteur – sonner – ma porte – apporter – un colis
→ _______________________________________________________________________.
2. Dimanche dernier – nous – jouer – tennis – dîner – avec - amis
3. Ils – prendre - taxi – 20h – retrouver – Lin – centre-ville – et - aller – théâtre - ensemble
4. Ma mère – faire – courses – rentrer – maison – cuisiner – repas délicieux
5. On – aller – Italie – visiter – beaucoup – villes – faire – une centaine de photos
6. Les manifestants – marcher – rues de Nantes - rester – tout l’après-midi
1. Il y a 10 min le facteur a sonné à ma porte, il m’a apporté un colis.
Article related
- Plus-que-parfait
- Futur simple
- Futur proche
- Exercise P1
- Exercise P2

- Connexion/Inscription
- LANGUE FRANÇAISE
- DICTIONNAIRES BILINGUES
- TRADUCTEUR
- CONJUGATEUR
- ENCYCLOPÉDIE
- CUISINE
- FORUM
- JEUX
- LIVRES
- Connexion/Inscription Newsletter
- Suivez nous:
- EN ES DE IT
Verbe intransitif du 1 er groupe / Auxiliaire avoir
Faire un ou des voyages, partir ailleurs, dans une autre région, un autre pays. Lire plus
Remarque : Le g devient -ge- devant a et o : je voyage, nous voyageons ; il voyagea .
- il, elle voyage
- nous voyageons
- vous voyagez
- ils, elles voyagent
- Imparfait
- je voyageais
- tu voyageais
- il, elle voyageait
- nous voyagions
- vous voyagiez
- ils, elles voyageaient
- Passé simple
- je voyageai
- tu voyageas
- il, elle voyagea
- nous voyageâmes
- vous voyageâtes
- ils, elles voyagèrent
- je voyagerai
- tu voyageras
- il, elle voyagera
- nous voyagerons
- vous voyagerez
- ils, elles voyageront
- Passé composé
- j' ai voyagé
- tu as voyagé
- il, elle a voyagé
- nous avons voyagé
- vous avez voyagé
- ils, elles ont voyagé
- Plus-que-parfait
- j' avais voyagé
- tu avais voyagé
- il, elle avait voyagé
- nous avions voyagé
- vous aviez voyagé
- ils, elles avaient voyagé
- Passé antérieur
- j' eus voyagé
- tu eus voyagé
- il, elle eut voyagé
- nous eûmes voyagé
- vous eûtes voyagé
- ils, elles eurent voyagé
- Futur antérieur
- j' aurai voyagé
- tu auras voyagé
- il, elle aura voyagé
- nous aurons voyagé
- vous aurez voyagé
- ils, elles auront voyagé
- que je voyage
- que tu voyages
- qu'il, qu'elle voyage
- que nous voyagions
- que vous voyagiez
- qu'ils, qu'elles voyagent
- que je voyageasse
- que tu voyageasses
- qu'il, qu'elle voyageât
- que nous voyageassions
- que vous voyageassiez
- qu'ils, qu'elles voyageassent
- que j' eusse voyagé
- que tu eusses voyagé
- qu'il, qu'elle eût voyagé
- que nous eussions voyagé
- que vous eussiez voyagé
- qu'ils, qu'elles eussent voyagé
- que j' aie voyagé
- que tu aies voyagé
- qu'il, qu'elle ait voyagé
- que nous ayons voyagé
- que vous ayez voyagé
- qu'ils, qu'elles aient voyagé
- CONDITIONNEL
- je voyagerais
- tu voyagerais
- il, elle voyagerait
- nous voyagerions
- vous voyageriez
- ils, elles voyageraient
- j' aurais voyagé
- tu aurais voyagé
- il, elle aurait voyagé
- nous aurions voyagé
- vous auriez voyagé
- ils, elles auraient voyagé
- ayons voyagé
- ayez voyagé
- avoir voyagé
- ayant voyagé
SYNONYMES bourlinguer (familier) - circuler - migrer - se déplacer
Recherche: 1 résultat(s)
verbe intransitif du 1 er groupe.
Conjugaison: Indicatif / Subjonctif / Conditionnel / Impératif / Infinitif / Participe /

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Conjugate the French verb voyager in all tenses: future, participle, present, indicative, subjunctive. Irregular verbs, auxiliary verbs, conjugation rules and conjugation models in French verb conjugation. Translate voyager in context, with examples of use and definition.
Conjugate the French verb voyager in several modes, tenses, voices, numbers, persons : indicative mode, subjunctive, imperative mood, conditional, participle form ...
Voyager french definition. VOYAGER : v. intr. Faire un voyage, se déplacer selon un itinéraire d'une certaine longueur à destination d'une autre ville, d'un autre pays. Il a bien voyagé, il a bien vu du pays. Voyager par toute l'Europe. Voyager en Italie, en Grèce, en Asie. Il a passé sa vie à voyager.
Visit the Progress with Lawless French Q+A forum to get help from native French speakers and fellow learners. Support Lawless French This free website is created with love and a great deal of work. If you love it, please consider making a one-time or monthly donation.. Your support is entirely optional but tremendously appreciated.
Conjugation table for voyager (to travel) in the present, passé composé, future, imperfect, conditional, subjunctive, plus-que-parfait and more. ... french verb conjugation tables PRESENTje voyagetu voyagesil voyagenous voyageonsvous voyagezils voyagentPASSÉ SIMPLEje voyageaitu voyageasil voyageanous voyageâmesvous voyageâtesils ...
'voyager' conjugation table in French. Indicative Subjunctive Imperative. Infinitive voyager. Past Participle
Règle du verbe voyager Le e des verbes en -ger est conservé après le g devant les voyelles a et o : nous mangeons, tu mangeas afin de maintenir partout le son du g doux. Réciproquement, les verbes en -guer conservent le u à toutes les formes : fatiguant, il fatigue.
Conjugate the verb voyager in all tenses: present, past, participle, present perfect, gerund, etc. Conjugation of voyager - French verb | PONS English
voyager Firefox and Chrome users : install a shortcut ( Firefox or Chrome ) then type "conj voyager" in your address bar for the fastest conjugations. It is conjugated like: manger
A list of the common conjugations for the French verb voyager, along with their English translations. This is a literary tense, i.e. a tense used in writing, in everyday speech the Passé Composé is used to refer to past actions. The French Future Perfect or Futur antérieur is made with the future tense of avoir or être and the past ...
La conjugaison du verbe voyager et ses synonymes. Conjuguer le verbe voyager à indicatif, subjonctif, impératif, infinitif, conditionnel, participe, gérondif.
All the conjugation of the verb : Conjugaison : voyager (verbe intransitif) Larousse ... voyager. Verbe intransitif du 1 er groupe / Auxiliaire avoir. Faire un ou des voyages, partir ailleurs, dans une autre région, un autre pays. Lire plus. Remarque : Le g devient -ge-devant a et o : je voyage, nous voyageons ; il voyagea.
French verb VOYAGER conjugated in all forms, with full audio, irregular highlighting, negative forms, and the English translation for all forms.
voyager. v. n. faire voyage, aller en pays éloigné. Il a bien voyagé, il a bien vu du pays. Voyager par toute l'Europe. Voyager en Italie, en Grèce, en Asie, etc. Les étrangers qui viennent voyager en France. Il a passé sa vie à voyager.
voyageant. Conjuguer le verbe voyager au présent, à l'imparfait, au passé simple, au futur,au conditionnel, à l'imperatif, au participe, passé composé, Plus-que-parfait.
Il devait voyager beaucoup en son temps..." ♪ He must have traveled greatly in his time ♪ "Accorde-toi du temps pour voyager avec un être aimé jusqu'à un endroit spécial." "make time to travel with a loved one to a special place." "Après toutes ces années à voyager sans répit, "j'allai enfin m'envoyer dans les airs.
Conjuguez le verbe voyager au passé antérieur à la troisième personne du singulier. Il en Europe pendant plusieurs semaines. Conjugaisons du verbe voyager au présent, passé, plus-que-parfait, imparfait, futur. Conjuguer voyager à l'indicatif, impératif, subjonctif, conditionnel, participe, gérondif etc.
Waiting for your reply. Voyager - Verb conjugation in French. Learn how to conjugate voyager in various tenses. Present: je voyage, tu voyages, il voyage ...
Conjugate the French Verb "Voyager". In French, the verb voyager means "to travel." This is easy to remember if you associate traveling with a voyage. When you want to say things such as "I traveled" or "we are traveling" in French, the verb needs to be conjugated. A short lesson will introduce you to the most basic conjugations of voyager .
How to conjugate the passé composé in French. To conjugate the passé composé we use the present tense of avoir or être as an auxiliary verb, followed by the past participle (participe passé) of the main verb. In negative sentences, the past participle comes after the second part of the negation (pas).
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like J'ai, Tu as, Il/Elle a and more.
2.1. The passé composé with "être". 2.1.1. Reflexive verbs. In the passé composé tense, the reflexive verb go with the auxiliary verb "être". The place of "être" is in between the reflexive pronoun and the past participle. When going with "être", the past participle must agree with the subject of the sentence.
voyager. Verbe intransitif du 1 er groupe / Auxiliaire avoir. Faire un ou des voyages, partir ailleurs, dans une autre région, un autre pays. Lire plus. Remarque : Le g devient -ge- devant a et o : je voyage, nous voyageons ; il voyagea. INDICATIF.