

13 Social impacts of tourism + explanations + examples
Understanding the social impacts of tourism is vital to ensuring the sustainable management of the tourism industry. There are positive social impacts of tourism, demonstrating benefits to both the local community and the tourists. There are also negative social impacts of tourism.
In this article I will explain what the most common social impacts of tourism are and how these are best managed. At the end of the post I have also included a handy reading list for anybody studying travel and tourism or for those who are interested in learning more about travel and tourism management.
The social impacts of tourism
Preserving local culture, strengthening communities, provision of social services, commercialisation of culture and art, revitalisation of culture and art, preservation of heritage, social change, globalisation and the destruction of preservation and heritage, loss of authenticity , standardisation and commercialisation, culture clashes, tourist-host relationships, increase in crime, gambling and moral behaviour, social impacts of tourism: conclusion, social impacts of tourism- further reading.
Firstly, we need to understand what is meant by the term ‘social impacts of tourism’. I have covered this in my YouTube video below!
To put it simply, social impacts of tourism are;
“The effects on host communities of direct and indirect relations with tourists , and of interaction with the tourism industry”
This is also often referred to as socio-cultural impacts.
Tourism is, at its core, an interactive service. This means that host-guest interaction is inevitable. This can have significant social/socio-cultural impacts.
These social impacts can be seen as benefits or costs (good or bad). I will explain these below.

Positive social impacts of tourism
There are many social benefits of tourism, demonstrating positive social impacts. These might include; preserving the local culture and heritage; strengthening communities; provision of social services; commercialisation of culture and art; revitalisation of customs and art forms and the preservation of heritage.

It is the local culture that the tourists are often coming to visit.
Tourists visit Beijing to learn more about the Chinese Dynasties. Tourists visit Thailand to taste authentic Thai food. Tourists travel to Brazil to go to the Rio Carnival, to mention a few…
Many destinations will make a conserved effort to preserve and protect the local culture. This often contributes to the conservation and sustainable management of natural resources, the protection of local heritage, and a renaissance of indigenous cultures, cultural arts and crafts.
In one way, this is great! Cultures are preserved and protected and globalisation is limited. BUT, I can’t help but wonder if this is always natural? We don’t walk around in Victorian corsets or smoke pipes anymore…
Our social settings have changed immensely over the years. And this is a normal part of evolution! So is it right that we should try to preserve the culture of an area for the purposes of tourism? Or should we let them grow and change, just as we do? Something to ponder on I guess…
Tourism can be a catalyst for strengthening a local community.
Events and festivals of which local residents have been the primary participants and spectators are often rejuvenated and developed in response to tourist interest. I certainly felt this was the way when I went to the Running of the Bulls festival in Pamplona, Spain. The community atmosphere and vibe were just fantastic!

The jobs created by tourism can also be a great boost for the local community. Aside from the economic impacts created by enhanced employment prospects, people with jobs are happier and more social than those without a disposable income.
Local people can also increase their influence on tourism development, as well as improve their job and earnings prospects, through tourism-related professional training and development of business and organisational skills.
Read also: Economic leakage in tourism explained

The tourism industry requires many facilities/ infrastructure to meet the needs of the tourist. This often means that many developments in an area as a result of tourism will be available for use by the locals also.
Local people often gained new roads, new sewage systems, new playgrounds, bus services etc as a result of tourism. This can provide a great boost to their quality of life and is a great example of a positive social impact of tourism.
Tourism can see rise to many commercial business, which can be a positive social impact of tourism. This helps to enhance the community spirit as people tend to have more disposable income as a result.
These businesses may also promote the local cultures and arts. Museums, shows and galleries are fantastic way to showcase the local customs and traditions of a destination. This can help to promote/ preserve local traditions.

Some destinations will encourage local cultures and arts to be revitalised. This may be in the form of museum exhibitions, in the way that restaurants and shops are decorated and in the entertainment on offer, for example.
This may help promote traditions that may have become distant.
Many tourists will visit the destination especially to see its local heritage. It is for this reason that many destinations will make every effort to preserve its heritage.
This could include putting restrictions in place or limiting tourist numbers, if necessary. This is often an example of careful tourism planning and sustainable tourism management.
This text by Hyung You Park explains the principles of heritage tourism in more detail.
Negative social impacts of tourism
Unfortunately, there are a large number of socio-cultural costs on the host communities. These negative social impacts include; social change; changing values; increased crime and gambling; changes in moral behaviour; changes in family structure and roles; problems with the tourist-host relationship and the destruction of heritage.

Social change is basically referring to changes in the way that society acts or behaves. Unfortunately, there are many changes that come about as a result of tourism that are not desirable.
There are many examples throughout the world where local populations have changed because of tourism.
Perhaps they have changed the way that they speak or the way that they dress. Perhaps they have been introduced to alcohol through the tourism industry or they have become resentful of rich tourists and turned to crime. These are just a few examples of the negative social impacts of tourism.
Read also: Business tourism explained: What, why and where

Globalisation is the way in which the world is becoming increasingly connected. We are losing our individuality and gaining a sense of ‘global being’, whereby we are more and more alike than ever before.
Globalisation is inevitable in the tourism industry because of the interaction between tourists and hosts, which typically come from different geographic and cultural backgrounds. It is this interaction that encourage us to become more alike.
Here are some examples:
- When I went on the Jungle Book tour on my travels through Goa, the tourists were giving the Goan children who lived in the area sweets. These children would never have eaten such sweets should they not have come into contact with the tourists.
- When I travelled to The Gambia I met a local worker (known as a ‘ bumster ‘) who was wearing a Manchester United football top. When I asked him about it he told me that he was given the top by a tourist who visited last year. If it was not for said tourist, he would not have this top.
- In Thailand , many workers have exchanged their traditional work of plowing the fields to work in the cities, in the tourism industry. They have learnt to speak English and to eat Western food. If it were not for the tourists they would have a different line of work, they would not speak English and they would not choose to eat burger and chips for their dinner!
Many people believe globalisation to be a bad thing. BUT, there are also some positives. Think about this…
Do you want an ‘authentic’ squat toilet in your hotel bathroom or would you rather use a Western toilet? Are you happy to eat rice and curry for breakfast as the locals would do or do you want your cornflakes? Do you want to struggle to get by when you don’t speak the local language or are you pleased to find somebody who speaks English?
When we travel, most tourists do want a sense of ‘familiar’. And globalisation helps us to get that!

You can learn more about globalisation in this post- What is globalisation? A simple explanation .

Along similar lines to globalisation is the loss of authenticity that often results from tourism.
Authenticity is essentially something that is original or unchanged. It is not fake or reproduced in any way.
The Western world believe that a tourist destination is no longer authentic when their cultural values and traditions change. But I would argue is this not natural? Is culture suppose to stay the same or it suppose to evolve throughout each generation?
Take a look at the likes of the long neck tribe in Thailand or the Maasai Tribe in Africa. These are two examples of cultures which have remained ‘unchanged’ for the sole purpose of tourism. They appear not to have changed the way that they dress, they way that they speak or the way that they act in generations, all for the purpose of tourism.
To me, however, this begs the question- is it actually authentic? In fact, is this not the exact example of what is not authentic? The rest of the world have modern electricity and iPhones, they watch TV and buy their clothes in the nearest shopping mall. But because tourists want an ‘authentic’ experience, these people have not moved on with the rest of the world, but instead have remained the same.
I think there is also an ethical discussion to be had here, but I’ll leave that for another day…
You can learn more about what is authenticity in tourism here or see some examples of staged authenticity in this post.
Read also: Environmental impacts of tourism
Similarly, destinations risk standardisation in the process of satisfying tourists’ desires for familiar facilities and experiences.
While landscape, accommodation, food and drinks, etc., must meet the tourists’ desire for the new and unfamiliar, they must at the same time not be too new or strange because few tourists are actually looking for completely new things (think again about the toilet example I have previously).
Tourists often look for recognisable facilities in an unfamiliar environment, like well-known fast-food restaurants and hotel chains. Tourist like some things to be standardised (the toilet, their breakfast, their drinks, the language spoken etc), but others to be different (dinner options, music, weather, tourist attractions etc).
Do we want everything to become ‘standardised’ though? I know I miss seeing the little independent shops that used to fill the high streets in the UK. Now it’s all chains and multinational corporations. Sure, I like Starbucks (my mug collection is coming on quite nicely!), but I also love the way that there are no Starbucks in Italy. There’s something great about trying out a traditional, yet unfamiliar coffee shop, or any independant place for that matter.
I personally think that tourism industry stakeholders should proceed with caution when it comes to ‘standardisation’. Sure, give the tourists that sense of familiar that they are looking for. But don’t dilute the culture and traditions of the destination that they are coming to visit, because if it feels too much like home….. well, maybe they will just stay at home next time? Just a little something to think about…

On a less philosophical note, another of the negative social impacts of tourism is that it can have significant consequences is culture clashes.
Because tourism involves movement of people to different geographical locations cultural clashes can take place as a result of differences in cultures, ethnic and religious groups, values, lifestyles, languages and levels of prosperity.
The attitude of local residents towards tourism development may unfold through the stages of euphoria, where visitors are very welcome, through apathy, irritation and potentially antagonism when anti-tourist attitudes begin to grow among local people. This is represented in Doxey’s Irritation Index, as shown below.
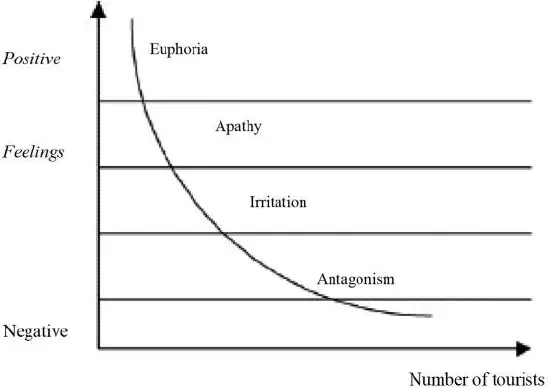
Culture clashes can also be exasperated by the fundamental differences in culture between the hosts and the tourists.
There is likely to be economic inequality between locals and tourists who are spending more than they usually do at home. This can cause resentment from the hosts towards the tourists, particularly when they see them wearing expensive jewellery or using plush cameras etc that they know they can’t afford themselves.
Further to this, tourists often, out of ignorance or carelessness, fail to respect local customs and moral values.
Think about it. Is it right to go topless on a beach if within the local culture it is unacceptable to show even your shoulders?
There are many examples of ways that tourists offend the local population , often unintentionally. Did you know that you should never put your back to a Buddha? Or show the sole of your feet to a Thai person? Or show romantic affection in public in the Middle East?
A little education in this respect could go a long way, but unfortunately, many travellers are completely unaware of the negative social impacts that their actions may have.
The last of the social impacts of tourism that I will discuss is crime, gambling and moral behaviour. Crime rates typically increase with the growth and urbanisation of an area and the growth of mass tourism is often accompanied by increased crime.
The presence of a large number of tourists with a lot of money to spend and often carrying valuables such as cameras and jewellery increases the attraction for criminals and brings with it activities like robbery and drug dealing.
Although tourism is not the cause of sexual exploitation, it provides easy access to it e.g. prostitution and sex tourism . Therefore, tourism can contribute to rises in the numbers of sex workers in a given area. I have seen this myself in many places including The Gambia and Thailand .
Lastly, gambling is a common occurrence as a result of tourism. Growth of casinos and other gambling facilities can encourage not only the tourists to part with their cash, but also the local population .
As I have demonstrated in this post, there are many social impacts of tourism. Whilst some impacts are positive, most unfortunately are negative impacts.
Hopefully this post on the social impacts of tourism has helped you to think carefully about the impacts that your actions may have on the local community that you are visiting. I also hope that it has encouraged some deeper thinking with regards to issues such as globalisation, authenticity and standardisation.
If you are interested in learning more about topics such as this subscribe to my newsletter ! I send out travel tips, discount coupons and some material designed to get you thinking about the wider impacts of the tourism industry (like this post)- perfect for any tourism student or keen traveller!
As you can see, the social impacts of tourism are an important consideration for all industry stakeholders. Do you have any comments on the social impacts of tourism? Leave your comments below.
If you enjoyed this article on the social impacts of tourism, I am sure that you will love these too-
- Environmental impacts of tourism
- The 3 types of travel and tourism organisations
- 150 types of tourism! The ultimate tourism glossary
- 50 fascinating facts about the travel and tourism industry
Social and cultural impacts
When we travel we consume places and local cultures. That can happen with more or less interaction with the local population. Maybe you only get to meet the hotel and restaurant staff? The influx of temporary visitors with other goals and means than the local population (see Behaviour on holiday) affects the local community and its inhabitants’ quality of life and culture, in the short and long term. Where tourism has grown exponentially many different positive and negative impacts have been noted, and the greater the dependence on tourism the community has, the more inclined locals and the local tourist industry are to change local traditions and lifestyles to adapt to tourists’ needs.
Local populations’ reactions to increased tourism occur in different ways. They have different strategies to adapt their day to day life around tourists. Some embrace development wholeheartedly. These are often locals with a connection to the tourism industry. Others create barriers, in other words they keep their distance from tourists and rarely interact. Locals might avoid touristy squares and streets. Other distancing strategies are withdrawal involving removing themselves completely from the area during the tourist season. Maybe you have another place to move to for the time being. An extreme strategy, appearing recently in Barcelona and Venice, for instance, is opposition. In this case tourism has affected their life quality very negatively, and the volume of tourism is so extreme that the local population demonstrate or act violently against tourism actors.
In a review of earlier research, Australian researchers listed the potential positive and negative impacts from a social perspective. In the table below is a selection of the most prominent:

It’s important to take into account potential social and cultural impacts when planning for tourism. Often the focus is on tourism as a tool for socio-economic development (money and jobs), but a majority of local residents more often come into direct contact with the impacts listed in the table above. The impacts are more obvious in less rural communities and in destinations where the distances (cultural, economic, powerful, etc.) between tourists and local residents are greater.
Ap, J., & Crompton, J. L. (1993). Residents' Strategies for Responding to Tourism Impacts. Journal of Travel Research, 32(1), 47-50. Deery, M., Jago, L., & Fredline, L. (2012). Rethinking social impacts of tourism research: A new research agenda. Tourism Management, 33(1), 64-73 Hunt, E. (2017, August 4). ‘Tourism kills neighbourhoods’: how do we save cities from the city break? The Guardian. www.theguardian.com. Lundberg, E. (2014). Tourism Impacts and Sustainable Development. Gothenburg: University of Gothenburg.

- Methodology

Maintained in cooperation with Travel CO 2
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, from success to unrest: the social impacts of tourism in barcelona.
International Journal of Tourism Cities
ISSN : 2056-5607
Article publication date: 11 January 2022
Issue publication date: 10 August 2022
This study aims to examine the main factors and the related impacts that have caused a negative shift in the social perception of tourism among residents of Barcelona. Namely, it contextualises the recent evolution of the impacts and the social perception of tourism among the city’s residents; analyses the relationship between the social perception of tourism and different tourist, real estate, demographic and economic factors; and lastly, it identifies the social impacts that majorly influence the negative perception among residents in every neighbourhood.
Design/methodology/approach
This study applies quantitative and qualitative techniques to a selection of five neighbourhoods of Barcelona. First, the character of the neighbourhoods was analysed, and external statistical information was later provided to understand the state and evolution of the factors that shape perceptions of tourism. Secondly, representatives of the community movements were interviewed in-depth. This consecutive qualitative approach enabled the comprehension of how these factors shape the residents’ perception.
The results showed that residents generally shared similar perceptions despite variations among neighbourhoods. Perceived negative effects included not only the most direct consequences of tourism such as anti-social behaviour and congestion of public spaces but also indirect ones such as population displacement and the weakening of social structures.
Originality/value
This study’s innovation lies in linking objective statistical data that describe the reality of a tourist neighbourhood (housing prices, number of available beds, family income, etc.), to the subjective perceptions of its residents. Thus, it is possible to identify the perceived impacts of tourism (which have an impact on the local population’s satisfaction), and relate these to the true evolution of tourism variables in the neighbourhood. This contrasted reading between perception and reality is important for future initiatives for the regulation of tourism in the city.
- Sustainable tourism
- Social impacts
- Residents’ perception
Elorrieta, B. , Cerdan Schwitzguébel, A. and Torres-Delgado, A. (2022), "From success to unrest: the social impacts of tourism in Barcelona", International Journal of Tourism Cities , Vol. 8 No. 3, pp. 675-702. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJTC-05-2021-0076
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2021, International Tourism Studies Association.
Related articles
All feedback is valuable.
Please share your general feedback
Report an issue or find answers to frequently asked questions
Contact Customer Support
Sustainable tourism
Related sdgs, promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable ....

Description
Publications.
Tourism is one of the world's fastest growing industries and an important source of foreign exchange and employment, while being closely linked to the social, economic, and environmental well-being of many countries, especially developing countries. Maritime or ocean-related tourism, as well as coastal tourism, are for example vital sectors of the economy in small island developing States (SIDS) and coastal least developed countries (LDCs) (see also: The Potential of the Blue Economy report as well as the Community of Ocean Action on sustainable blue economy).
The World Tourism Organization defines sustainable tourism as “tourism that takes full account of its current and future economic, social and environmental impacts, addressing the needs of visitors, the industry, the environment and host communities".
Based on General assembly resolution 70/193, 2017 was declared as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development.
In the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development SDG target 8.9, aims to “by 2030, devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”. The importance of sustainable tourism is also highlighted in SDG target 12.b. which aims to “develop and implement tools to monitor sustainable development impacts for sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”.
Tourism is also identified as one of the tools to “by 2030, increase the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries” as comprised in SDG target 14.7.
In the Rio+20 outcome document The Future We want, sustainable tourism is defined by paragraph 130 as a significant contributor “to the three dimensions of sustainable development” thanks to its close linkages to other sectors and its ability to create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities. Therefore, Member States recognize “the need to support sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building that promote environmental awareness, conserve and protect the environment, respect wildlife, flora, biodiversity, ecosystems and cultural diversity, and improve the welfare and livelihoods of local communities by supporting their local economies and the human and natural environment as a whole. ” In paragraph 130, Member States also “call for enhanced support for sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building in developing countries in order to contribute to the achievement of sustainable development”.
In paragraph 131, Member States “encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small- and medium-sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential”. In this regard, Member States also “underline the importance of establishing, where necessary, appropriate guidelines and regulations in accordance with national priorities and legislation for promoting and supporting sustainable tourism”.
In 2002, the World Summit on Sustainable Development in Johannesburg called for the promotion of sustainable tourism development, including non-consumptive and eco-tourism, in Chapter IV, paragraph 43 of the Johannesburg Plan of Implementation.
At the Johannesburg Summit, the launch of the “Sustainable Tourism – Eliminating Poverty (ST-EP) initiative was announced. The initiative was inaugurated by the World Tourism Organization, in collaboration with UNCTAD, in order to develop sustainable tourism as a force for poverty alleviation.
The UN Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD) last reviewed the issue of sustainable tourism in 2001, when it was acting as the Preparatory Committee for the Johannesburg Summit.
The importance of sustainable tourism was also mentioned in Agenda 21.
For more information and documents on this topic, please visit this link
UNWTO Annual Report 2016
In December 2015, the United Nations General Assembly declared 2017 as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development. This is a unique opportunity to devote a year to activities that promote the transformational power of tourism to help us reach a better future. This important cele...
UNWTO Annual Report 2015
2015 was a landmark year for the global community. In September, the 70th Session of the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a universal agenda for planet and people. Among the 17 SDGs and 169 associated targets, tourism is explicitly featured in Goa...
Emerging Issues for Small Island Developing States
The 2012 UNEP Foresight Process on Emerging Global Environmental Issues primarily identified emerging environmental issues and possible solutions on a global scale and perspective. In 2013, UNEP carried out a similar exercise to identify priority emerging environmental issues that are of concern to ...
Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
This Agenda is a plan of action for people, planet and prosperity. It also seeks to strengthen universal peace in larger freedom, We recognize that eradicating poverty in all its forms and dimensions, including extreme poverty, is the greatest global challenge and an indispensable requirement for su...
Towards Measuring the Economic Value of Wildlife Watching Tourism in Africa
Set against the backdrop of the ongoing poaching crisis driven by a dramatic increase in the illicit trade in wildlife products, this briefing paper intends to support the ongoing efforts of African governments and the broader international community in the fight against poaching. Specifically, this...
Status and Trends of Caribbean Coral Reefs: 1970-2012
Previous Caribbean assessments lumped data together into a single database regardless of geographic location, reef environment, depth, oceanographic conditions, etc. Data from shallow lagoons and back reef environments were combined with data from deep fore-reef environments and atolls. Geographic c...
15 Years of the UNWTO World Tourism Network on Child Protection: A Compilation of Good Practices
Although it is widely recognized that tourism is not the cause of child exploitation, it can aggravate the problem when parts of its infrastructure, such as transport networks and accommodation facilities, are exploited by child abusers for nefarious ends. Additionally, many other factors that contr...
Natural Resources Forum: Special Issue Tourism
The journal considers papers on all topics relevant to sustainable development. In addition, it dedicates series, issues and special sections to specific themes that are relevant to the current discussions of the United Nations Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD)....

Thailand: Supporting Sustainable Development in Thailand: A Geographic Clusters Approach
Market forces and government policies, including the Tenth National Development Plan (2007-2012), are moving Thailand toward a more geographically specialized economy. There is a growing consensus that Thailand’s comparative and competitive advantages lie in amenity services that have high reliance...
Natural Resources Forum, a United Nations Sustainable Development Journal (NRF)
Natural Resources Forum, a United Nations Sustainable Development Journal, seeks to address gaps in current knowledge and stimulate relevant policy discussions, leading to the implementation of the sustainable development agenda and the achievement of the Sustainable...
Road Map on Building a Green Economy for Sustainable Development in Carriacou and Petite Martinique, Grenada
This publication is the product of an international study led by the Division for Sustainable Development (DSD) of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA) in cooperation with the Ministry of Carriacou and Petite Martinique Affairs and the Ministry of Environment, Foreig...
UN Ocean Conference 2025
Our Ocean, Our Future, Our Responsibility “The ocean is fundamental to life on our planet and to our future. The ocean is an important source of the planet’s biodiversity and plays a vital role in the climate system and water cycle. The ocean provides a range of ecosystem services, supplies us with
UN Ocean Conference 2022
The UN Ocean Conference 2022, co-hosted by the Governments of Kenya and Portugal, came at a critical time as the world was strengthening its efforts to mobilize, create and drive solutions to realize the 17 Sustainable Development Goals by 2030.
58th Session of the Commission for Social Development – CSocD58
22nd general assembly of the united nations world tourism organization, world tourism day 2017 official celebration.
This year’s World Tourism Day, held on 27 September, will be focused on Sustainable Tourism – a Tool for Development. Celebrated in line with the 2017 International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development, the Day will be dedicated to exploring the contribution of tourism to the Sustainable Deve
World Tourism Day 2016 Official Celebration
Accessible Tourism for all is about the creation of environments that can cater for the needs of all of us, whether we are traveling or staying at home. May that be due to a disability, even temporary, families with small children, or the ageing population, at some point in our lives, sooner or late
4th Global Summit on City Tourism
The World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) and the Regional Council for Tourism of Marrakesh with support of the Government of Morroco are organizing the 4th Global Summit on City Tourism in Marrakesh, Morroco (9-10 December 2015). International experts in city tourism, representatives of city DMOs, of
2nd Euro-Asian Mountain Resorts Conference
The World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) and Ulsan Metropolitan City with support of the Government of the Republic of Korea are organizing the 2nd Euro-Asian Mountain Resorts Conference, in Ulsan, Republic of Korea (14 - 16 October 2015). Under the title “Paving the Way for a Bright Future for Mounta
21st General Assembly of the United Nations World Tourism Organization
Unwto regional conference enhancing brand africa - fostering tourism development.
Tourism is one of the Africa’s most promising sectors in terms of development, and represents a major opportunity to foster inclusive development, increase the region’s participation in the global economy and generate revenues for investment in other activities, including environmental preservation.
- January 2017 International Year of Tourism In the context of the universal 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the International Year aims to support a change in policies, business practices and consumer behavior towards a more sustainable tourism sector that can contribute to the SDGs.
- January 2015 Targets 8.9, 12 b,14.7 The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development commits Member States, through Sustainable Development Goal Target 8.9 to “devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”. The importance of sustainable tourism, as a driver for jobs creation and the promotion of local culture and products, is also highlighted in Sustainable Development Goal target 12.b. Tourism is also identified as one of the tools to “increase [by 2030] the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries”, through Sustainable Development Goals Target 14.7.
- January 2012 Future We Want (Para 130-131) Sustainable tourism is defined as a significant contributor “to the three dimensions of sustainable development” thanks to its close linkages to other sectors and its ability to create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities. Therefore, Member States recognize “the need to support sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building that promote environmental awareness, conserve and protect the environment, respect wildlife, flora, biodiversity, ecosystems and cultural diversity, and improve the welfare and livelihoods of local communities” as well as to “encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small and medium sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential”.
- January 2009 Roadmap for Recovery UNWTO announced in March 2009 the elaboration of a Roadmap for Recovery to be finalized by UNWTO’s General Assembly, based on seven action points. The Roadmap includes a set of 15 recommendations based on three interlocking action areas: resilience, stimulus, green economy aimed at supporting the tourism sector and the global economy.
- January 2008 Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria The Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria represent the minimum requirements any tourism business should observe in order to ensure preservation and respect of the natural and cultural resources and make sure at the same time that tourism potential as tool for poverty alleviation is enforced. The Criteria are 41 and distributed into four different categories: 1) sustainability management, 2) social and economic 3) cultural 4) environmental.
- January 2003 1st Int. Conf. on Climate Change and Tourism The conference was organized in order to gather tourism authorities, organizations, businesses and scientists to discuss on the impact that climate change can have on the tourist sector. The event took place from 9 till 11 April 2003 in Djerba, Tunisia.
- January 2003 WTO becomes a UN specialized body By Resolution 453 (XV), the Assembly agreed on the transformation of the WTO into a United Nations specialized body. Such transformation was later ratified by the United Nations General Assembly with the adoption of Resolution A/RES/58/232.
- January 2002 World Ecotourism Summit Held in May 2002, in Quebec City, Canada, the Summit represented the most important event in the framework of the International Year of Ecosystem. The Summit identified as main themes: ecotourism policy and planning, regulation of ecotourism, product development, marketing and promotion of ecotourism and monitoring costs and benefits of ecotourism.
- January 1985 Tourism Bill of Rights and Tourist Code At the World Tourism Organization Sixth Assembly held in Sofia in 1985, the Tourism Bill of Rights and Tourist Code were adopted, setting out the rights and duties of tourists and host populations and formulating policies and action for implementation by states and the tourist industry.
- January 1982 Acapulco Document Adopted in 1982, the Acapulco Document acknowledges the new dimension and role of tourism as a positive instrument towards the improvement of the quality of life for all peoples, as well as a significant force for peace and international understanding. The Acapulco Document also urges Member States to elaborate their policies, plans and programmes on tourism, in accordance with their national priorities and within the framework of the programme of work of the World Tourism Organization.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1. History and Overview
1.5 Impacts of Tourism
As you can already see, the impacts of the global tourism industry today are impressive and far reaching. Let’s have a closer look at some of these outcomes.
Tourism Impacts
Tourism can generate positive or negative impacts under three main categories: economic, social, and environmental. These impacts are analyzed using data gathered by businesses, governments, and industry organizations.
Economic Impacts
According to the 2019 edition of the UNWTO International Tourism Highlights report , international tourist arrivals reached 1.4 billion, a 5% increase in 2018. UNWTO Secretary-General Zurab Pololikashvili stated that the sheer growth of the industry was driven by a strong global economy, surge of the travel-ready middle class from emerging economies, technological advances, and more affordable travel costs among others (UNWTO, 2019). At the same time, the UNWTO (2019) reported export earnings from tourism, or the sum of international tourism receipts and passenger transport, reached a staggering USD 1.7 trillion. This demonstrates that the industry is a major economic engine of growth and development.
Europe has traditionally been the region with the highest tourism dollar spending with USD 570 billion, followed by Asia and the Pacific (USD 435 billion), the Americas (USD 334 billion), Middle East (USD 73 billion), and Africa (USD 38 billion). Asia has shown to have the strongest growths in both arrivals (+7%) and spending (+7%). Africa equally shared a +7% growth in arrivals, suggesting a new interest in travelling to the continent.
What are the trends that are motivating people to travel? The six consumer travel trends, according to the UNWTO (2019) include:
- Travel “to change” or focusing on more authentic travel, transformation, and living like a local.
- Travel “to show” or capturing “instagramable” moments, experiences, and visiting selfie-worthy destinations.
- Pursuit of a healthy life or engaging into active travel that involves walking, wellness, and sports tourism.
- Rise of the “access” economy.
- Solo travel and multigenerational travel as a result of single households and an aging population.
- Rising awareness on travel with sustainable advocacies, thoughtful consideration about climate change impacts, and plastic-free travel.
Social Impacts
Because tourism experiences also involve human interaction, certain impacts may occur. Generally, social impacts in tourism are related to guest-to-host or host-to-guest influences and changes. Studies of these encounters often relate to the Social Exchange Theory, which describe how tourists and hosts’ behaviours change as a result of the perceived benefits and threats they create during interaction (Nunkoo, 2015).
Positive social impacts in tourism include learning about different cultures, increasing tolerance and inclusion through LGBTQ+ travel, increasing amenities (e.g., parks, recreation facilities), investment in arts and culture, celebration of Indigenous peoples , and community pride. When developed conscientiously, tourism can, and does, contribute to a positive quality of life for residents and a deeper learning and appreciation for tourists.

Unfortunately, tourism also has its shortcomings and is culpable for some detrimental impacts. However, as identified by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP, 2003a), negative social impacts of tourism can include:
- Change or loss of indigenous identity and values
- Culture clashes
- Physical causes of social stress (increased demand for resources)
- Ethical issues (such as an increase in sex tourism or the exploitation of child workers)
Some of these issues are explored in further detail in Chapter 12 , which examines the development of Indigenous tourism in British Columbia.
Environmental Impacts
Tourism relies on, and greatly impacts, the natural environment in which it operates. In many cases, the environment is an essential resource that outdoor recreation and ecotourism cannot exist without. Even though many areas of the world are conserved in the form of parks and protected areas, tourism development can still have severe negative impacts from misuse, overuse, and neglect. According to UNEP (2003b), these can include:
- Depletion of natural resources (water, forests, etc.)
- Pollution (air pollution, noise, sewage, waste and littering)
- Physical impacts (construction activities, marina development, trampling, loss of biodiversity)
The environmental impacts of tourism knows no boundaries and can reach outside local areas and have detrimental effects on the global ecosystem. One example is increased emissions from necessary tourism elements such as transportation. Air travel for instance, is a major contributor to climate change. Chapter 10 looks at the environmental impacts of tourism in more detail.
A overview of the negative and positive impacts:
Whether positive or negative, tourism is a force for change around the world that is capable of transforming the environment from micro- to macro-scales at a staggering rate.
Media Attributions
- Pride by Mercedes Mehling is licensed under an Unsplash Licence .
Groups specially protected in international or national legislation as having a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory, and their cultural or historical distinctiveness from other populations. Indigenous peoples are recognized in the Canadian Constitution Act as comprising three groups: First Nations, Métis, and Inuit.
Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC - 2nd Edition Copyright © 2015, 2020, 2021 by Morgan Westcott and Wendy Anderson, Eds is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Campus Maps
Events Research Spotlight Series #4 - Harnessing the social impacts of tourism
Research Spotlight Series #4 - Harnessing the social impacts of tourism
Tourism has tremendous social impacts on local communities’ lives and livelihoods in destinations. Community well-being and Quality of Life (QoL) need a deeper understanding of perceived social impacts. Understanding social impacts of tourism on host communities is also vital in the context of tourism planning and Community Based Tourism (CBT) development. Community perception of social benefits and costs results in potential hospitable or hostile response to tourists and tourism development. Harnessing the social benefits and reducing the social costs of tourism is significant for destinations resulting in a more sustainable tourism development.
This is a hybrid event
- To attend in person, complete the form at the bottom of this page
- To attend online, click HERE
- Introduction by Dr Zilmiyah Kamble
- Presentation by Dr Zilmiyah Kamble
- Q&A session
- End of Event
Photos and recording will be taken during the event for news and various publicity purposes
Registration information collected here will be handled in accordance with the Privacy Policy of the Singapore campus of James Cook University.
Register for this event

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Understanding the social impacts of tourism is vital to ensuring the sustainable management of the tourism industry. There are positive social impacts of tourism, demonstrating benefits to both the local community and the tourists. There are also negative social impacts of tourism. In this article I will explain what the most common social ...
unities.Endnotes1: The direct impact of the Travel & Tourism sector is the main focus of this report, although supply chain ("indirect") and worker spending ("induced") impacts are included in some findings to illustrate the wider reach th. t the sector has.2: Young workers are defined here as those aged 1.
Abstract. Residents' overall well-being and quality-of-life require a deeper understanding of their perceived social impacts of tourism to determine appropriate management strategies to promote behaviours in support of tourism development. Aligning with the 2030 Agenda for sustainable development, this paper proposes a new framework for ...
The social impact of tourism was assessed using 8 items with four-point scales (4 = a great amount, 3 = a moderate amount, 2 = a little amount, and 1 = no effect at all). ... The introduction of these modern transportation systems is due to the tourism industry. However, the impact of tourism on the expansion of the infrastructure is not up to ...
This paper aims to systematically review and analyze the current research on tourism impacts on destinations during 2016-2020. The Scopus database was used to search for tourism impact studies ...
The development of tourism induces changes in the social character of a destination. Tourism is a globalized business activity and thus presents growing challenges in terms of traditional social culture. With the continuous development of the tourism industry, traditional social culture has changed dramatically at many World Heritage sites (WHSs). Additionally, the growing dependence of many ...
1. Introduction. Tourism economic impact studies are regularly conducted to estimate the industry's contribution to economic growth and development (Comerio & Strozzi, 2019).As addressed by the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), it is globally recognized that regional development should aim for environmental, economic and sociocultural sustainability (UN, 2020).
The Social Impacts of Tourism (English version) This background paper has three objectives. First to identify the most common social impacts arising from tourism development. Second, to suggest reasons why negative impacts occur. Third, to suggest policies and strategies for countries to adopt in the 21ist century to mitigate these negative ...
Research into the social impacts of tourism has much to learn from the experience of organisational culture and, as Tucker, McCoy, and Evans (1990) argue, a qualitative paradigm provides flexibility, adaptiveness, depth, realism and has face validity that a quantitative approach may not provide.
The Social Impacts of Tourism (English version) Published: 1997 Pages: 44. eISBN: 978-92-844-1096-5. Abstract: This background paper has three objectives. First to identify the most common social impacts arising from tourism development. Second, to suggest reasons why negative impacts occur.
Social and cultural impacts of tourism are the ways in which tourism is contributing to changes in value systems, individual behaviour, family relationships, collective life styles, moral conduct, creative e expressions, traditional ceremonies and community organization. In other words they are the effects on the people of host communities of ...
Scope. The 'Social Impact of Tourism' section of Frontiers in Sustainable Tourism publishes cutting-edge, timely, and high-quality critical research across the field of tourism studies, exploring its connections with wider social and cultural processes and underlying structures. The section is led by two specialty chief editors, who are active ...
Originality/value. This work engages with the novel concept of "socialising tourism". In connecting this new theory to the older theory of "tourism as a social force", this paper considers how COVID-19 has offered a possible transformative moment to enable more just and sustainable tourism futures.
Tourism impacts tourist destinations in both positive and negative ways, encompassing economic, political, socio-cultural, environmental, and psychological dimensions. Economic effects: Increased tax revenue, personal income growth, enhanced The impacts of tourism , and the creation of additional employment opportunities.
Various models and frameworks have been developed over the years to measure and better understand the social impacts of tourism. Smith's model of cross-cultural contact (Pearce, Citation 1994) argued that the social impact of tourism is directly linked to the types of tourist who visit a destination (Woodside et al., Citation 2009). The larger ...
It's important to take into account potential social and cultural impacts when planning for tourism. Often the focus is on tourism as a tool for socio-economic development (money and jobs), but a majority of local residents more often come into direct contact with the impacts listed in the table above. The impacts are more obvious in less ...
positive tourism impacts relat ing to the social w e ll-being of. the community as the stimulation of infrastructure. development (road s, communications, healthcare, educat ion, public transport ...
CSR initiatives in the tourism industry comprise two major dimensions: community and the environment. Concern for the environment has emerged as one of the key initiatives of the tourism industry (i.e., environment-driven initiatives, such carbon offsetting, anti-poaching initiatives and ecological restoration).
Regional Wine and Beverage Tourism: Social and Economic Development Perspectives. Agritourism and Local Development: Innovations, Collaborations, and Sustainable Growth. UN World's Indigenous Peoples Day: Indigenous Tourism and Cultural Revitalization: Impacts, Opportunities, and Collaborative Approaches. Learn more about Research Topics.
This study aims to examine the main factors and the related impacts that have caused a negative shift in the social perception of tourism among residents of Barcelona. Namely, it contextualises the recent evolution of the impacts and the social perception of tourism among the city's residents; analyses the relationship between the social ...
Tourism is one of the world's fastest growing industries and an important source of foreign exchange and employment, while being closely linked to the social, economic, and environmental well-being of many countries, especially developing countries. Maritime or ocean-related tourism, as well as coastal tourism, are for example vital sectors of the economy in small island developing States ...
The debate on the positive and negative social and cultural impacts of tourism has been a. common reemerging i ssue that surround t ourism development and sustainability. Tourism. development is ...
1.5 Impacts of Tourism As you can already see, the impacts of the global tourism industry today are impressive and far reaching. Let's have a closer look at some of these outcomes. Tourism Impacts. Tourism can generate positive or negative impacts under three main categories: economic, social, and environmental.
Research Spotlight Series #4 - Harnessing the social impacts of tourism Tourism has tremendous social impacts on the lives and livelihoods of local communities. Understanding these social impacts is vital for effective tourism planning and developing Community-Based Tourism. Enhancing the positive effects while reducing the negative ones can lead to more sustainable tourism growth.